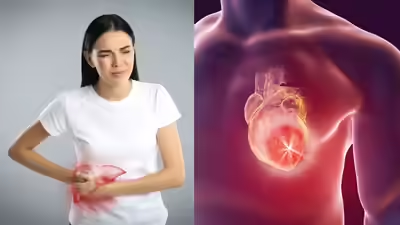
Fat liver disease, including metabolic dysfunction -associated steatotic liver disease (MasLD), is increasingly recognized as a major global health problem. Although it mainly affects the liver, research shows that it also has significant effects on general health, especially the heart. People with oily liver are at higher risk of developing cardiovascular problems such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease and heart failure. Factors such as chronic inflammation, insulin resistance and altered lipid metabolism connect liver fat accumulation to heart health. Early detection, lifestyle changes and medical management are crucial to reducing the risks and protecting both liver and heart function.
Understanding oily liver disease and its connection to heart disease
Fat liver disease occurs when excess fat is collected in liver cells. In Masld, this condition occurs in individuals without significant alcohol consumption, often linked to obesity, type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. The disease progresses through stages:
- Simple steatosis: fat accumulation without inflammation.
- Non-alcohol Steatohepatitis (NASH): Fat accompanying accompanied by inflammation and liver cell damage.
- Cirrhos: Severe scarring in the liver tissue.
- Liver cancer: development of malignant cells in the liver.
Early stages often constitute no symptoms, which makes early discovery challenging.
Heart conditions caused by oily liver disease
Emerging Research indicates a robust relationship between oily liver disease and various cardiovascular states:AtherosclerosisFat liver disease contributes to the construction of plaque in arteries, which leads to reduced and hardened arteries. This occurs because excess fat in the liver can increase systemic inflammation and promote the accumulation of cholesterol -rich blood vessels deposits. Over time, these plaque reduces blood flow, increases blood pressure and significantly increases the risk of stroke and heart attack. A study published in Hypertension Discusses how non-alcoholic bold liver disease (NAFLD) is a risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, which is the main cause of death in patients with NAFL.Coronary artery diseaseIndividuals with oily liver have a higher risk of developing blockages in the coronary carts, which deliver blood to the heart muscle. The combination of insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and chronic inflammation associated with oily liver accelerates the development of CAD. This can manifest itself as chest pain (angina), shortness of breath or, in severe cases, a heart attack. A study published in Lancet Regional Health -Europa emphasizes that metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), a severe form of oily liver disease, can lead to liver scarring (fibrosis), cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease and liver cancerHeart failureFat liver disease can increase the risk of heart failure, a condition where the heart cannot pump blood effectively to meet the body’s needs. Chronic metabolic stress from oily liver can lead to structural and functional changes in the heart, including thickening of the heart walls (left ventricular hypertrophy) and reduced heart efficiency. People with oily liver are also more likely to develop high blood pressure, which further contributes to heart failure risk.ArrhythmiasA study in Nature examines gastroenterology and hepatology Investigates the risk of cardiomyopathy and cardiac arrhythmias in patients with non -alcoholic fatty liver disease, which highlights the underlying mechanisms and clinical implications. The presence of oily liver is linked to an increased risk of abnormal heart rhythms, including atrial fibrillation. Systemic inflammation, oxidative stress and electrolytobalances associated with oily liver can interfere with the electrical signaling of the heart. Arrhythmias can increase the risk of stroke, reduce heart efficiency and in severe cases lead to sudden cardiac arrest.Noteworthy, cardiovascular disease has become the main cause of death in individuals with oily liver disease and exceeds liver-related complications
Mechanisms that connect fat live to heart disease
Several mechanisms explain the relationship between oily liver disease and cardiovascular state:
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation of the liver can lead to systemic inflammation, which affects blood vessels and heart tissue.
- Insulin resistance: Fatty liver is often associated with insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes, which is a significant risk factor for heart disease.
- Dyslipidemia: Changed lipid metabolism in oily liver disease leads to increased levels of harmful cholesterol and triglycerides, which contributes to plaque formation in arteries.
- Oxidative stress: Excess fat in the liver can produce reactive oxygen species, damage blood vessels and heart tissue.
These factors collectively increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease in individuals with oily liver.
The meaning of early detection and handling
Given the asymptomatic nature of fat disease at an early stage, regular screening is crucial, especially for individuals with risk factors such as obesity, diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Early discovery enables rapid intervention, which may include lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes, increased physical activity and weight management. In some cases, medicines may be prescribed to manage associated conditions such as diabetes and high cholesterol.Disclaimer clause: This article is only for information purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your health routine or treatment.Also read | Anal cancer: 5 major symptoms that every adult should know; bleeding, lumps and more