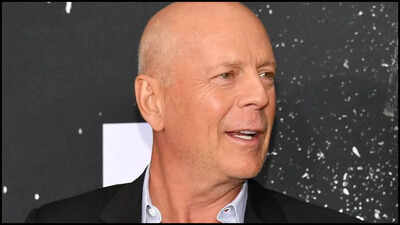
Bruce WillisThe “Die Hard” star, fights against Frontotemporal dementia (FTD). The beloved actor was diagnosed with the progressive heart disease about two years ago. Before this, he was diagnosed with Afasi 2022, which makes it difficult to communicate. His wife Emma Heming recently shared an update on Willi’s health. “Bruce is still very mobile. Bruce is in really good health overall. It is only his brain that fails with him,” she said in a conversation with ABC Special.
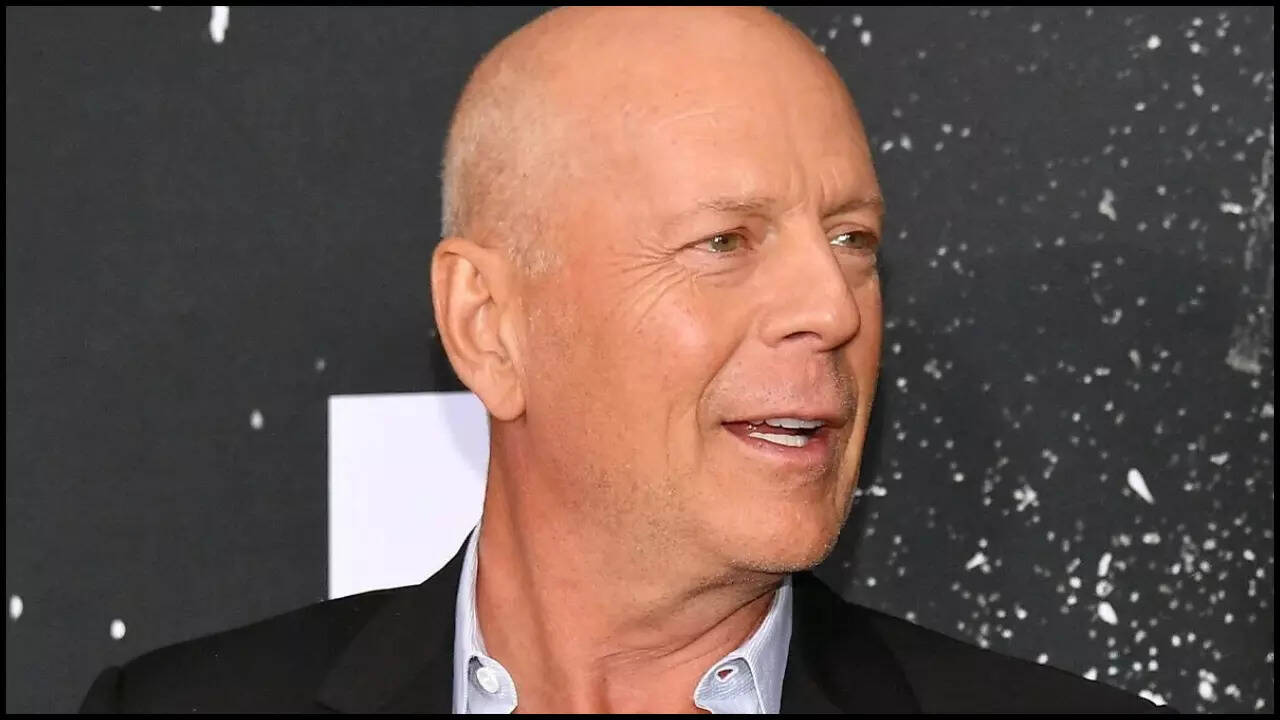

Here is everything you need to know about the rare state that Bruce Willis has.
What is Frontotemporal dementia?

Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is a neurological disorder that occurs when nerve cells in the front of the brain and temporal lobes are lost. This causes the lobes to shrink. These areas of brain control personality, emotions, behavior and speech.FTD is not a condition but a group of disorders that can affect behavior, personality, language and movement. This is one of the most common dementia that occurs in younger people. The symptoms occur between 40 and 65 years. But it can also occur in the elderly. It can affect both women and men equally.
Types of FTD

Frontotemporal disorders are grouped into three types, defined by the earliest symptoms.
- Behavioral variant FTD: This is the most common type of FTD and the person can experience. They act strangely around others and can cause embarrassing social situations.
- Primary progressive aphasia: This affects the ability to communicate. This includes challenges when it comes to using languages to speak, read, write and understand what others say. When it comes to aphasia, the person may experience difficulties in using or understanding words and may also have been spoken.
- Movement -related FTD: This occurs when the parts of the brain that control the movement are damaged.
Other types include:
- Frontotemporal dementia with Parkinsonism
What are the symptoms?

The symptoms of FTD Depends on which part of the brain it is affected. In the early stages, it can be difficult to identify the type, as the symptoms and the order they operate can vary from one person to another. The same symptoms can also occur for different disorders and vary from one stage of the disease to the next as different parts of the brain are affected.Here are some of the symptoms of behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvftd), the most common type.
- Challenges in planning and sequencing
- Difficulty in prioritizing tasks or activities
- Repeat the same activity or say the same words over and over
- Apathy
- Lack of empathy
- Reduced self -awareness
- Act impulsively or say or do unsuitable things without considering how others perceive the behavior
- Become uninterested in family or activities they used to care about
- Showing flat, exaggerated or erroneous feelings that appear to be connected from the situation
- Difficulty reading social signals, seems to lack empathy
- Compulsively eat or take food from other people’s plates
In some people, these symptoms can be accompanied by physical symptoms, for example:
- Shaking
- Muscle spasms or weakness
- Stiffness
- Poor coordination or balance
- Problem with swallowing
How can the condition be diagnosed?
The condition is often difficult to diagnose, as it is similar to the symptoms of other diseases, such as Alzheimer’s or mood disorders such as depression. However, a doctor may identify the condition based on the following:
- Performing an examination and looking at the symptoms
- Personal Medical History and Family History
- Laboratory tests
- Genetic testing
- By evaluating behavior, memory, thinking, language skills and physical function
- Brain image
Unfortunately, there is no treatment to cure, or slow down FTD, only the symptoms are treated.